Details & Benefits of Intragastric Balloon Surgery
A durable balloon fills the space in the stomach to reinforce proper portion control. The procedure is non-surgical and takes a half hour or less. Under a sedative, your sendoscopist advances a thin tube (catheter) containing the balloon into your stomach. The FDA-approved implant helps patients lose weight without invasive surgery. Mercy specialists provide comprehensive support to help you maintain your results.
Controlling Blood Pressure
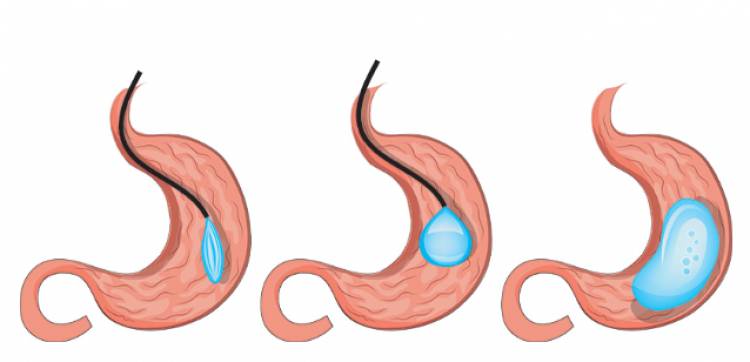
To make you feel full and encourage portion control, it works by taking up space in the stomach. The balloon is a temporary device that your Mercy gastroenterologist inserts in a quick and easy outpatient procedure without making any incisions or stitches. During the procedure, your gastroenterologist will use medication to relax and numb your throat before advancing an endoscope down your throat into your stomach and esophagus. Once they confirm there are no conditions that would prevent the insertion of the balloon, they will advance it and attach it to a catheter. It is then filled with saline, and the balloon is placed in your stomach.
The ORBERA balloon is made of soft, durable silicone. It occupies stomach space, reducing the food you can eat anytime. Once the balloon is inserted, your Mercy team will guide you through a personalized diet and exercise program to help you retrain your appetite and adopt new eating habits. In addition, your gastroenterologist will monitor you for any potential side effects of the treatment, such as nausea and vomiting.
Weight Loss
A gastric balloon is a soft, latex-free balloon placed without surgery into the stomach. It is filled with saline fluid and expands to the size of a grapefruit. The balloon takes up space in the stomach to make you feel full after eating smaller meals and to encourage portion control. In addition, the balloon triggers stomach stretch receptors to slow the passage of food and liquids. The treatment normally takes 20 to 30 minutes. You are placed under sedation for the placement of the balloon but can return home shortly afterward. Nausea and vomiting may occur immediately after the procedure but will subside as your stomach adjusts to the balloon's presence. During recovery, you will remain on a clear liquid diet.
You must continue following a healthy, balanced diet and exercise regimen for the balloon's life, which is removed after six months. Studies have shown that the gastric balloon is a secure and reliable non-surgical therapeutic option for patients with a BMI over 30 who desire to reduce their weight or reduce their risk of obesity-related health problems like diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and joint discomfort. It can also be used as a bridging procedure for bariatric surgery if you still decide to commit to the permanent surgical option.
Controlling Blood Sugar
The Elipse balloon is made from a soft, pliable silicone material to minimize irritation to the stomach wall. The procedure is non-surgical and takes about an hour. The doctor may prescribe a moderate sedative for your comfort and to promote relaxation. The physician inserts a flexible telescope (endoscope) down the back of your throat to your stomach and places the balloon in the pouch. Once in place, the balloon fills up space in your stomach, making you feel full and encouraging portion control. You will be on a liquid diet the first week, then move to a soft food plan such as protein shakes or puddings. You can start eating regular foods within three weeks of the procedure. Besides weight loss, the intragastric balloon also helps control diabetes and hypertension. The balloon reduces the sugar the blood absorbs and lowers glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. The weight loss team will work with you to retrain your appetite and establish healthy lifestyle habits that lead to lasting success. We are committed to providing the tools and support you need to get your life back on track.
Controlling Diabetes
The intragastric balloon, inflated with saline, takes up space in the stomach and reduces how much food can be eaten. It also helps people feel full faster, making them less hungry between meals.
The inflated balloon can be removed at any time without any permanent changes to the anatomy of the stomach. After 1-2 weeks, patients resume a normal, soft diet and are gradually allowed to add solid foods as they progress. The balloon is not intended to provide a long-term solution, and it is recommended that patients seek professional dietary advice for continued success.
Before the balloon is placed, a specially-trained gastroenterologist advances an endoscope down the throat into the stomach and esophagus, where the uninflated balloon is then advanced. The balloon is positioned over the opening of the stomach and anchored in place using a catheter that contains a filling tube. The balloon is filled with saline, which expands it to the size of a grapefruit or softball. The process takes about a half-hour; patients are normally discharged one to two hours after the procedure.











